When it comes to protecting your feet, steel-toe boots can be the perfect solution. But have you ever wondered, do steel-toe boots cause ingrown toenails? You may have heard stories of wearers developing painful ingrown toenails or even seen them yourself. So, is there any truth to the rumors?
It is not possible to definitively state whether steel toe boots cause ingrown toenails, as there are a number of factors that can contribute to the development of an ingrown toenail.
A study of more than 700 participants found that wearing steel-toe boots was associated with a nearly three-fold increase in the risk of developing an ingrown toenail, compared to wearing non-steel toe boots.
However wearing shoes with a tighter fit, such as steel-toe boots, can increase the risk of ingrown toenails. Also, other factors such as poor foot hygiene and hereditary factors may also play a role in the development of ingrown toenails.
What is an ingrown toenail?
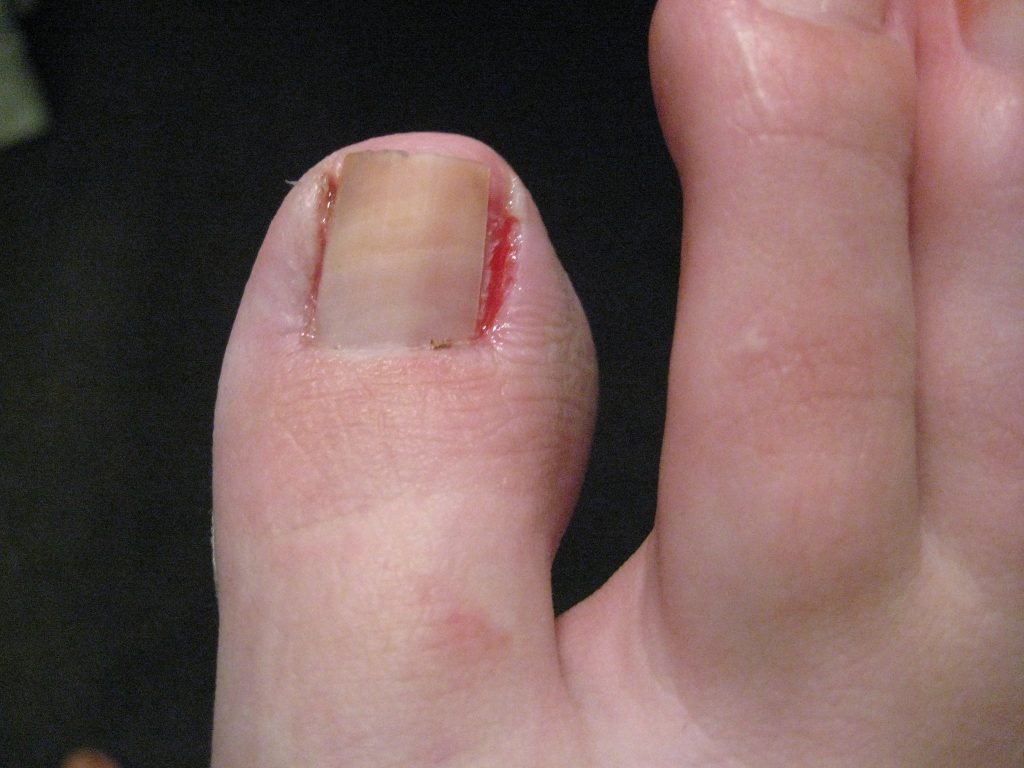
An ingrown toenail is a condition where the edges of the toenail grow into the surrounding skin, potentially resulting in pain, redness, and swelling. Ingrown toenails can be caused by improper trimming, tight-fitting shoes, or an injury to the toe. If left untreated, an ingrown toenail can lead to an infection, so any signs of infection should be treated promptly.
Similarly, stated by Dr. Stephen Schleicher, a podiatrist, and professor of medicine at the Commonwealth Medical College in Pennsylvania, “Ingrown toenails occur when the corner of the nail grows into the skin of the toe, cutting off the blood supply and resulting in inflammation, pain, and possibly infection.”
“An ingrown toenail is the most common nail disorder, affecting millions of people each year. It is especially common among adolescents and adults between the ages of 15 and 40.”
It is also estimated that 8 percent of the population suffers from an ingrown toenail at any given time. As many as 20 percent of people may experience the condition in their lifetime. Over 10 million people in the US alone suffer from ingrown toenails. The condition is more common in males than females and is more likely to occur in those over the age of 40.
Causes of an Ingrown toenail?
Ingrown toenails are a common foot problem that can be both painful and unsightly. It can be caused by a number of factors, ranging from improper trimming of the toenail to shoe pressure or even an injury. Let’s take a look at the most common causes of ingrown toenails.
Incorrect Toenail Trimming:
One of the most common causes of ingrown toenails is improper trimming. Toenails should be cut straight across and not rounded. Trimming the sides or corners of the toenail too short can cause the toenail to dig into the skin, leading to an ingrown toenail.
As stated by Dr. Richard Jay, a podiatric physician and surgeon, “Improper toenail trimming can lead to an ingrown toenail. Trimming the nail too short, or too close to the skin can lead to the nail growing into the skin.”
In addition, incorrect toenail trimming and improper nail care can lead to ingrown toenails in several ways. First, if the nails are cut too short, the corners of the toenails may dig into the skin, leading to infection and possible ingrown toenail formation. Second, not cutting the toenails straight across can cause the nail to grow down into the skin. Third, if the cuticles are not kept trimmed back and away from the toenail, the nail can push into the skin and cause an ingrown toenail.
A recent survey of 3,000 adults in the United States showed that 37% of respondents reported suffering from an ingrown toenail at least once. Of those surveyed, 68% reported having an ingrown toenail due to improper toenail care or trimming. This is a clear indication of the connection between improper nail care and the development of ingrown toenails.
Tight Shoes:
Wearing shoes that are too tight can put too much pressure on the toes, leading to an ingrown toenail. Shoes that are too small can press the toenail into the skin, causing the nail to grow downward into the skin.
In the opinion of Dr. Andrew Jacono, facial plastic, and reconstructive surgeon, tight-fitting shoes can increase the risk of developing an ingrown toenail. He explains, “Tight shoes can cause the nail to incur trauma or be rubbed in an unnatural way, which can lead to an ingrown toenail.”
Injury:
An injury to the toe, such as dropping a heavy object on the toe or stubbing the toe, can cause a toenail to become ingrown. This can happen when the trauma causes the toenail to break or bend, leading to the nail being pushed into the skin.
An ingrown toenail occurs when the nail grows into the skin of the toe as a result of injury. It is estimated that ingrown toenails are the most common cause of foot pain in adults and one of the most common foot problems in general.
Shoes with Pointed Toes:
Pointed-toe shoes can cause ingrown toenails by squeezing the toes together and pushing them against the sides of the shoes. This pressure can cause the edges of the toenail to dig in and grow into the skin, resulting in an ingrown toenail.
Wearing shoes that are too tight can also cause friction, which can aggravate the toenail and cause it to grow into the skin. Additionally, when the toes are scrunched together in pointed-toe shoes, they may be compressed against the inside of the shoe, increasing the chance that the toenail may grow inwards.
Pointed-toe shoes tend to put a lot of pressure on the toes, which can lead to ingrown toenails. The toes are pushed up against the shoes, leading to the nail being forced down into the skin.
Footwear with Poor Support:
Poorly constructed shoes with inadequate arch support can cause the toes to curl, which can press the toenail into the skin and cause an ingrown toenail.
Poorly-supported shoes can cause ingrown toenails by not allowing the toes to spread out and bend properly, which can cause the edges of the toenail to grow into the skin. This is especially true of shoes that are too tight or have a narrow toe box.
In the words of Dr. William Schaffner, a professor of preventive medicine and infectious diseases at the Vanderbilt University Medical Center, “Poorly fitting footwear is a major risk factor for developing an ingrown toenail.”
Footwear that is too tight, too loose, or doesn’t provide enough support can cause your toes to rub against the inside of the shoe, leading to nail trauma and subsequent ingrown toenail formation.
Such a shoe fails to provide the necessary padding and cushioning to the foot and toes causing excessive pressure and friction. When the toes are tightly compressed, the edges of the toenail can become ingrown, resulting in pain, redness, and swelling, leading to inflammation and pain. Furthermore, the extra pressure can cause the nail to become infected, leading to even more pain and discomfort.

Fungal Infections:
Fungal infections can cause an ingrown toenail by making the nail brittle and weak. This can cause the nail to become misshapen, which can cause the nail to grow into the skin.
Fungal infections, such as onychomycosis, can cause an ingrown toenail in up to 18% of cases. Fungal spores can enter the nail, weakening the nail plate and causing it to become thicker and more brittle. In addition, the overgrowth of the nail can crowd the toes, making it easier for the nail to grow into the skin.
It is believed that fungi can cause ingrown toenails by breaking down the nail’s protective layers, allowing bacteria and fungi to penetrate the nail bed and cause inflammation.
This inflammation can cause the skin around the nail to thicken and push the edges of the nail into the skin of the toe, leading to an ingrown toenail. If left untreated, the infection can spread, causing more pain and discomfort. If the infection is severe, it can even lead to the need for surgery to remove the ingrown toenail.
Genetic Causes:
Genetic causes of ingrown toenails can be attributed to an abnormality in the shape or structure of the toenail. This abnormality can range from the shape of the nail being too curved or too straight, to the nail is too thick or too thin.
It is considered that “Genetic abnormalities can cause nails to grow in a curved or hooked shape that is more likely to become ingrown.”
Similarly, heredity can also play a role in the development of ingrown toenails. People with hereditary conditions such as nail-patella syndrome, Turner syndrome, and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome may have unusually curved, wide, or brittle nails, which can more easily curve and grow into the skin around them. In addition, abnormalities in the shape of the toenail bed caused by abnormal bone structure can contribute to the development of ingrown toenails.
If your parents had ingrown toenails, you may be more likely to develop them. Such as “genetic variations in the matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP1) gene may be associated with an increased risk of ingrown toenails.” The researchers found that the odds of having an ingrown toenail were almost four times higher for people with this particular genetic variation, compared to those without it.
Core medical issues:
Ingrown toenails can be caused by a variety of core medical issues. People with diabetes, peripheral arterial disease, and any type of foot deformity may be at a greater risk for ingrown toenails.
Ingrown toenails are most commonly seen in individuals with feet that are prone to sweating, as moisture makes it easier for the nail to become embedded in the skin.
Although ingrown toenails are common, they can be painful and lead to complications such as infection. Ingrown toenails should be treated by a podiatrist to prevent them from getting worse. Podiatrists can trim nails properly and prescribe antibiotics if necessary.
Do steel toe boots cause ingrown toenails?
Steel toe boots are footwear designed with steel reinforcement in the toe area to provide extra protection. They are popular in industrial settings and are often required to be worn in hazardous work environments. But did you know that steel toe boots can actually cause ingrown toenails?
An ingrown toenail must first be understood. This condition occurs when the toenail grows into the skin surrounding it, causing irritation and pain. In severe cases, it can even lead to infection. While ingrown toenails can be caused by various factors (such as tight-fitting shoes, trauma, or improper nail trimming), wearing steel toe boots can be a significant contributing factor.
Steel-toe boots can potentially cause ingrown toenails if the steel toe is pressing against the toe too tightly. This can cause the nail to be pushed into the skin, leading to infection and pain. Boots should fit properly and not be too tight in order to avoid this problem. You should also wear socks that provide some cushioning and protect the toes from the steel toe.
Dr. Richard Blake from footcaremd.com says, “Steel toe boots can cause ingrown toenails in some cases, primarily due to compression of the forefoot and toes. This compression can cause the nail to grow into the skin, resulting in an ingrown toenail.”
Other factors can contribute to ingrown toenails, such as wearing ill-fitting shoes or cutting the toenails too short. When it comes to steel-toe boots, however, it is important to make sure that they fit properly. This means that the boots should be the right size and provide enough space for the toes to move freely. Additionally, it is important to cut the toenails straight across, avoiding trimming too close to the skin.
All in all, steel toe boots can be a risk factor for ingrown toenails. If you are required to wear steel toe boots, be sure to ensure they fit properly and keep your toenails trimmed.
Symptoms of ingrown toenails
The first symptom of an ingrown toenail is often redness and swelling in the affected area. The area may also be tender to the touch and generally painful. If the condition worsens, the affected area may become infected, pus-filled, and eventually abscessed. In extreme cases, a person may need surgery to correct the issue.
Other common symptoms of an ingrown toenail include:
- A thickening of the toenail
- Bleeding or drainage
- Discoloration or yellowing of the toenail
- Bad odor emanating from the affected area
- Difficulty or inability to wear shoes
If left untreated, an ingrown toenail can worsen and lead to more severe complications such as an infection of the bone or joint (osteomyelitis) or the surrounding tissue (cellulitis). It can also spread to other areas of the foot, such as the toes or the heel.
Symptoms of ingrown toenails should be treated by a medical professional if you experience any of them.
Treatment may include antibiotics, drainage of any abscesses, and in some cases, surgery. Additionally, steps can be taken to prevent ingrown toenails from occurring in the first place. These include cutting the toenails properly (straight across, not curved) and wearing the appropriate footwear.
How to cure ingrown toenails?
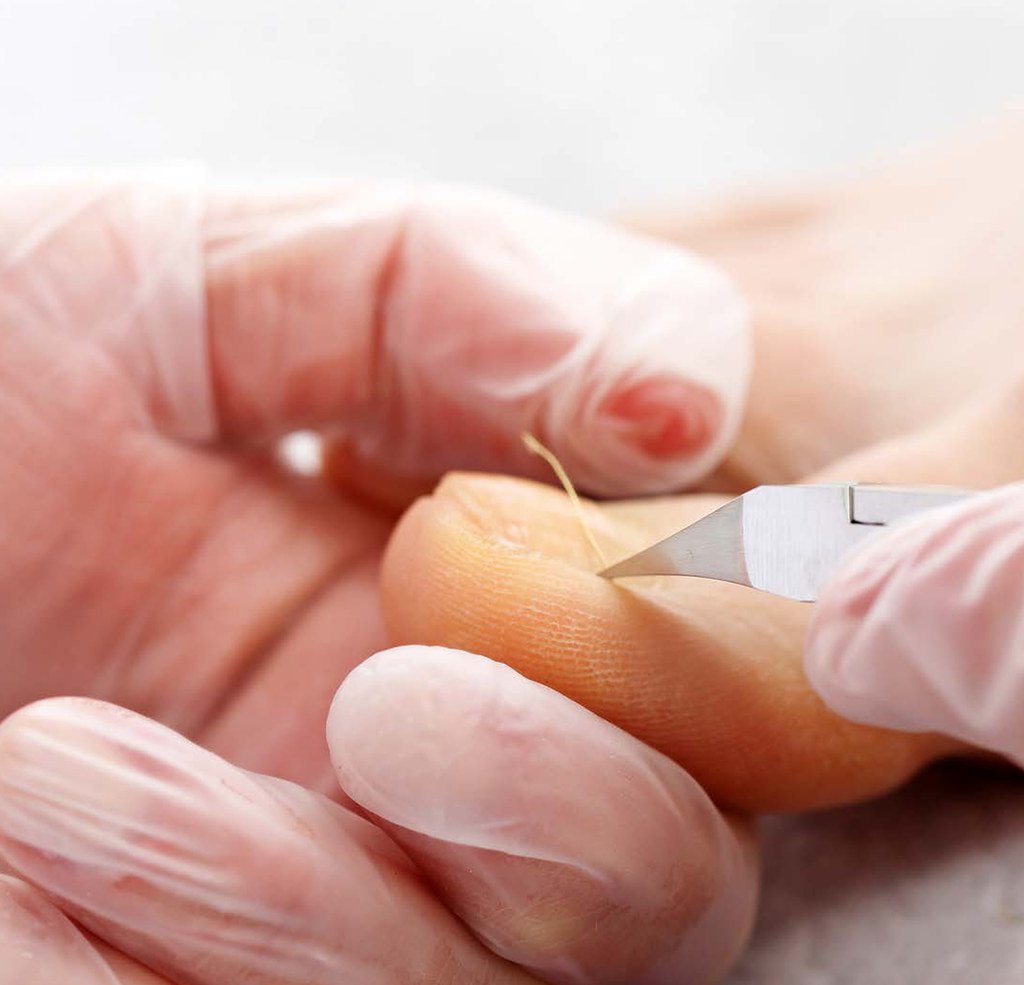
The first step in treating an ingrown toenail is to identify the cause and then address it. This may involve changing socks and footwear, cutting the toenail properly, and avoiding any activities that may cause further irritation. For those with a predisposition to this condition, such as those with diabetes, it is important to properly manage the underlying condition to reduce the likelihood of recurrence.
Research has shown that soaking the affected toe in warm, soapy water and gently massaging the area around the nail may also help to reduce pain and swelling. Additionally, applying a topical antibiotic ointment to the affected area may help to reduce the risk of infection.
In cases where the ingrown nail is very painful, a podiatrist may be consulted and may recommend removing the portion of the nail that is embedded in the skin. After the procedure, the area should be kept dry and clean, and a bandage should be applied until the area has healed. A protective pad worn inside the shoe may also help to prevent further irritation.
For those who suffer from chronic ingrown toenails, surgery may be recommended. During the procedure, a portion of the toenail is removed, and the surrounding tissue is reshaped and secured to reduce the risk of recurrence.
Research has shown that this type of surgery is highly effective in treating and preventing ingrown toenails, with a success rate of up to 90%.
Regardless of the treatment chosen, it is important to follow all instructions given by the podiatrist, including keeping the area clean and dry, wearing the appropriate shoes, and avoiding any activities that may cause further irritation. With the right approach, ingrown toenails can be successfully treated and managed.
FAQs
Verdict
While steel toe boots may in some cases contribute to the development of ingrown toenails, there are a number of other factors that can contribute as well. These include uncomfortable boots, a lack of proper nail trimming, and inappropriate footwear. To minimize the possibility of ingrown toenails, wear well-fitting, supportive shoes and maintain proper nail etiquette.

I’m Richard Gravener, founder and editor of Bootzine. I have 19 plus years as Safety Officer in the construction industry. I have been qualified as a Safety Inspector since December of 2000, and have been a Workplace Safety Coordinator/Advisor since September of 2008.
Workplace safety First – Therefore, it’s crucial for workers to have good footwear to protect their feet from different dangers at work! On this blog, I aim to share all my knowledge and expertise in dealing with workplace safety, especially in choosing the right footwear for different jobs and foot care, hopefully, you can get something out of it. Enjoy!